News

2022-01-26 分类:行业动态
When building an electronic circuit, you will use many basic electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, inductors, and integrated circuits. The following is a brief overview of the components and their functions.
Resistor: a resistor is one of the components you will encounter in an integrated circuit. As the name suggests, the device can resist current. Resistors are graded according to their rated power (the amount of power they can handle without explosion) and resistance value (the ability to resist current). Measurements are made in units called ohms. The electronic symbol of the unit is o.
Capacitors: these components can temporarily store charge. There are different types of these components, the most common being electrolytic discs and ceramic discs. The capacity of components is usually expressed in microfarads (µ f).
Diode: the diode only allows current to flow in one direction. Each diode has two terminals, called anode and cathode. When the anode is charged with a positive voltage and the cathode is charged with a negative voltage, the current can flow. Reversing these voltages will prevent current flow.
Transistors: these components are easily identified by their three terminals. In order for the components to work, a voltage must be applied to one of them; Base terminal. The base can then control the current in the other two terminals (emitter and collector).
Inductors: These are passive components that store energy in the form of a magnetic field. An inductor consists only of a coil wound around a magnetic core. The core can be a magnet or air. When an electric current passes through an inductor, a magnetic field is generated around it. If a magnet is used as the core, the magnetic field will be stronger.
Integrated circuit: integrated circuit refers to special equipment with all components required by electronic circuit. The assembly has diodes, transistors and other devices, all etched on a small piece of silicon. These components are used in many electronic devices, including watches and computers.
Microcontroller: a microcontroller is a small computer used to control a variety of devices, such as power tools, remote controls, medical equipment and office machines.
Transformer: it is composed of two coils. The transformer is usually used for step-up or step-down power supply.
Battery: the battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The two different batteries of the battery are anode (+) and cathode (-).
Fuses: fuses help prevent overloading of components due to excessive current. The fuse consists of connector, bracket, contact and metal fuse material (such as zinc or copper).
Relay: these electromechanical switches can turn on or off the power supply. The relay consists of electromagnet, armature, a series of electrical contacts and springs.
Switch: the switch interrupts the current. The four types of switches are: single pole single throw (SPST), single pole double throw (SPDT), double pole single throw (DPST) and double pole double throw (DPDT).
Motor: the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include rotor, stator, bearing, conduit box, shell and eyebolt.
Circuit breaker: as a protective device, the circuit breaker can be controlled by remote switch. It is designed to protect the circuit from overload or short circuit.
Resistor: a resistor is one of the components you will encounter in an integrated circuit. As the name suggests, the device can resist current. Resistors are graded according to their rated power (the amount of power they can handle without explosion) and resistance value (the ability to resist current). Measurements are made in units called ohms. The electronic symbol of the unit is o.
Capacitors: these components can temporarily store charge. There are different types of these components, the most common being electrolytic discs and ceramic discs. The capacity of components is usually expressed in microfarads (µ f).
Diode: the diode only allows current to flow in one direction. Each diode has two terminals, called anode and cathode. When the anode is charged with a positive voltage and the cathode is charged with a negative voltage, the current can flow. Reversing these voltages will prevent current flow.
Transistors: these components are easily identified by their three terminals. In order for the components to work, a voltage must be applied to one of them; Base terminal. The base can then control the current in the other two terminals (emitter and collector).
Inductors: These are passive components that store energy in the form of a magnetic field. An inductor consists only of a coil wound around a magnetic core. The core can be a magnet or air. When an electric current passes through an inductor, a magnetic field is generated around it. If a magnet is used as the core, the magnetic field will be stronger.
Integrated circuit: integrated circuit refers to special equipment with all components required by electronic circuit. The assembly has diodes, transistors and other devices, all etched on a small piece of silicon. These components are used in many electronic devices, including watches and computers.
Microcontroller: a microcontroller is a small computer used to control a variety of devices, such as power tools, remote controls, medical equipment and office machines.
Transformer: it is composed of two coils. The transformer is usually used for step-up or step-down power supply.
Battery: the battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The two different batteries of the battery are anode (+) and cathode (-).
Fuses: fuses help prevent overloading of components due to excessive current. The fuse consists of connector, bracket, contact and metal fuse material (such as zinc or copper).
Relay: these electromechanical switches can turn on or off the power supply. The relay consists of electromagnet, armature, a series of electrical contacts and springs.
Switch: the switch interrupts the current. The four types of switches are: single pole single throw (SPST), single pole double throw (SPDT), double pole single throw (DPST) and double pole double throw (DPDT).
Motor: the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include rotor, stator, bearing, conduit box, shell and eyebolt.
Circuit breaker: as a protective device, the circuit breaker can be controlled by remote switch. It is designed to protect the circuit from overload or short circuit.
Prev:Guide for ferrite beads
Next:
Copyright © 2022 SSF GROUP(ASIA) LIMITED 粤ICP备19078955号

QQ Chat

Wechat
Scan QR code and add customer

SSF provides the electronic components you need. SSF representative will contact you within 24 hours on product pricing and supply.
Name
Email
Phone
Demand
Code 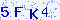
Submit
Cancel







 MTA32ATF4G64HZ-2G6B2 SODIMM DDR4 MICROM
MTA32ATF4G64HZ-2G6B2 SODIMM DDR4 MICROM